Blood group and genotype are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing. In simple terms, blood group refers to the classification of blood based on the presence or absence of certain antigens on the surface of red blood cells, while genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual that determines their traits and characteristics.
Blood Group
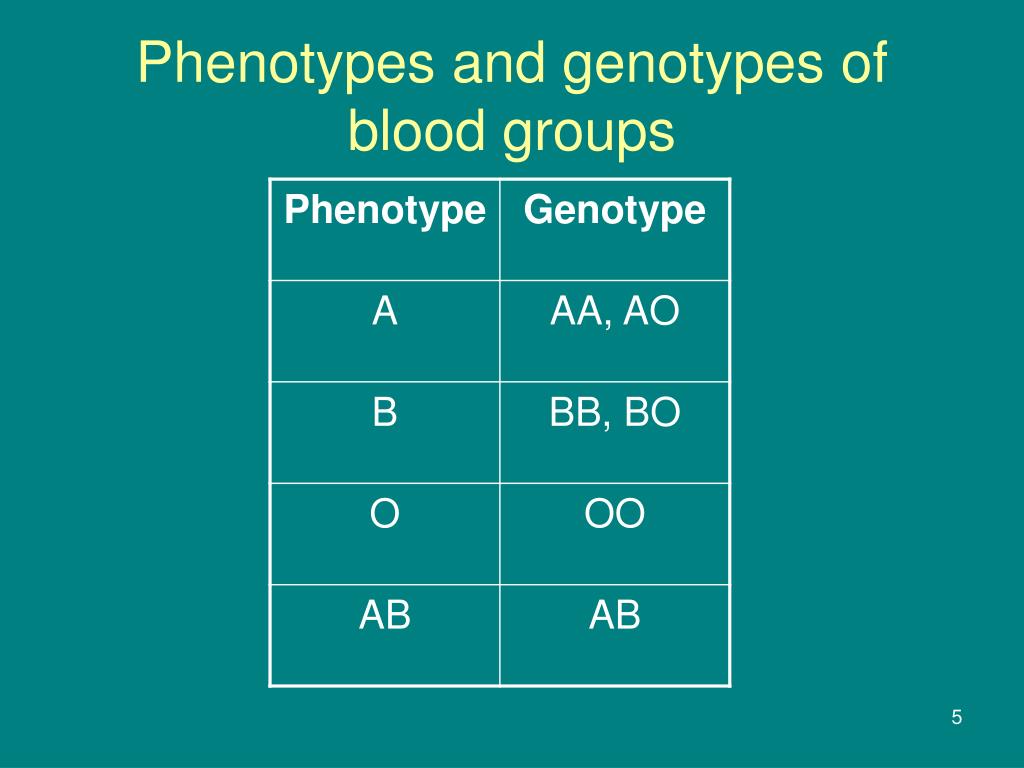
There are four main blood groups: A, B, AB, and O. Each of these blood groups is determined by the presence or absence of certain antigens on the surface of red blood cells. Antigens are substances that can trigger an immune response in the body.
Blood group A has antigen A on the surface of red blood cells, blood group B has antigen B, blood group AB has both antigens A and B, and blood group O has neither antigen. In addition to these antigens, blood also contains antibodies that can attack antigens that are not present on the surface of red blood cells.
Blood group is important in blood transfusions because if a person receives blood from a donor with an incompatible blood group, their immune system can attack the donor's red blood cells, leading to a potentially fatal reaction. For example, a person with blood group A can receive blood from a donor with blood group A or O, but not from a donor with blood group B or AB.
Genotype
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual that determines their traits and characteristics. This includes the genes that determine blood group, as well as other traits such as eye color, height, and susceptibility to certain diseases.
Genes come in pairs, with one copy inherited from each parent. The combination of these genes determines an individual's genotype. For example, the gene for blood group A is dominant over the gene for blood group O. This means that if a person inherits one copy of the gene for blood group A and one copy of the gene for blood group O, their blood group will be A.
Genotype is important in understanding the inheritance of genetic diseases. Some genetic diseases are caused by a single gene mutation, while others are caused by multiple genes interacting with each other and with environmental factors. Understanding an individual's genotype can help identify their risk of developing certain diseases and inform decisions about genetic testing and treatment.
How Blood Group and Genotype Are Related
While blood group and genotype are not the same thing, they are related. Blood group is determined by the presence or absence of certain antigens on the surface of red blood cells, which are determined by the genes inherited from parents. This means that a person's blood group is determined by their genotype.
However, not all genes that determine blood group are the same. There are multiple genes involved in the determination of blood group, and the specific combination of these genes can vary between individuals. This means that two people with the same blood group may have different genotypes.

In addition, blood group and genotype can interact with each other in certain situations. For example, some genetic mutations can affect the expression of antigens on the surface of red blood cells, leading to changes in blood group. This can complicate blood transfusions and require more detailed testing to ensure compatibility.
Conclusion
While blood group and genotype are related, they are not the same thing. Blood group refers to the classification of blood based on the presence or absence of certain antigens on the surface of red blood cells, while genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual that determines their traits and characteristics. Understanding the difference between these two terms is important in fields such as medicine and genetics, where they are used to inform decisions about treatment and testing.